Wi-Fi Sensing - A strategic enabler that improves safety and efficiency across industries
1️⃣ Background
The rapid growth of IoT, smart buildings, and healthcare technologies demands solutions that go beyond traditional connectivity. Organizations no longer just want to connect devices — they need real-time insights into movements, presence, and behaviors within physical spaces.
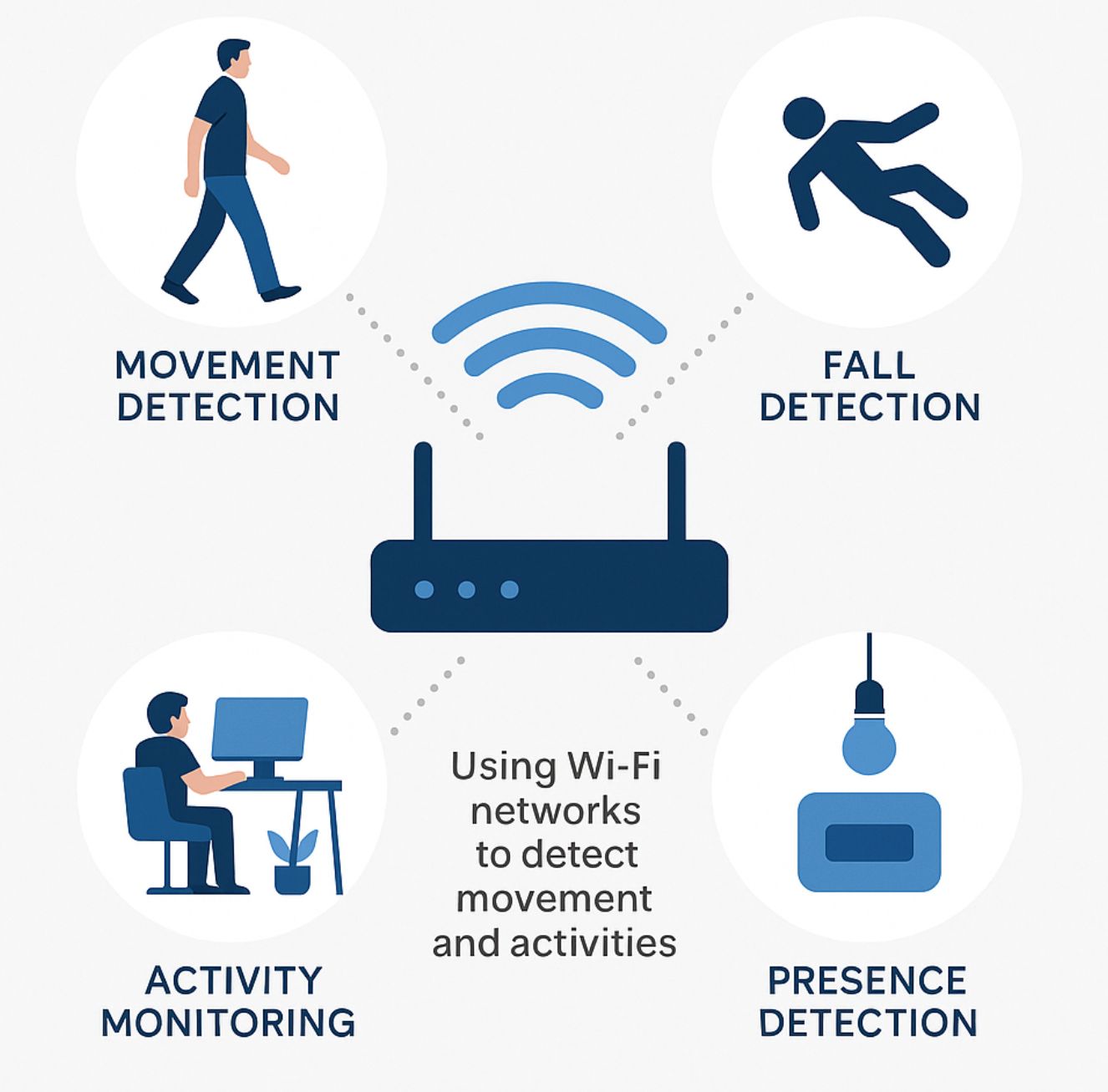
Traditional sensing technologies (e.g., cameras, motion detectors) present challenges such as high costs, privacy concerns, and complex deployment. Wi-Fi Sensing provides a scalable and privacy-friendly alternative: leveraging existing Wi-Fi networks to detect presence, movement, and activities.
2️⃣ Objective
The goal of implementing Wi-Fi Sensing is to:
- Enhance safety in healthcare, office, and industrial environments.
- Improve operational efficiency through better space and energy utilization.
- Optimize customer and employee experience with intelligent, context-aware services.
3️⃣ Scope
This business case focuses on three primary verticals:
- Healthcare – fall detection, patient activity monitoring, contactless supervision.
- Smart Buildings & Offices – replacing occupancy sensors with Wi-Fi-based detection for meeting rooms, workspaces, and HVAC optimization.
- Retail & Hospitality – analyzing customer flows, reducing waiting times, and supporting dynamic staff planning.
4️⃣ Urgency
- Cost Savings: leverage existing Wi-Fi infrastructure, reducing the need for additional cabling or expensive cameras.
- Privacy: no visual or audio data is collected; fully GDPR-compliant.
- Future-Proof: ready for integration with AI/ML for self-learning analytics and automation.
- Competitive Advantage: early adopters can deliver innovative services and safety features that create immediate business value.
5️⃣ Solution
Wi-Fi Sensing uses variations in Wi-Fi signals (Channel State Information – CSI) to detect movement or presence. By applying AI/ML models, organizations can differentiate between:
- Presence (whether someone is in the room)
- Activity (walking, sitting, falling)
- Behavioral patterns (foot traffic, time-based activity trends)
Integration with existing systems:
- Healthcare: integration with nurse call systems and electronic health records (EHR).
- Building Management: integration with BMS and HVAC platforms.
- Retail: integration with analytics dashboards and loyalty applications.
6️⃣ Financial Case (example)
- Investment: software licenses, AI engine, configuration & training.
- Savings: reduced physical sensors (up to 40%), energy savings through HVAC optimization, lower incident costs (healthcare).
- ROI: depending on the sector, typically achievable within 12–24 months.
7️⃣ Risks & Mitigation
- Technical adoption: mitigate through pilots and phased rollout.
- Privacy concerns: clear communication and compliance validation.
- Accuracy/interference: mitigate with AI/ML tuning and professional Wi-Fi design.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi Sensing is more than a technological innovation — it is a strategic enabler that improves safety, efficiency, and experience across industries.
Curious to learn more? Schedule a call or visit.
If you would like to know what we would be able to offer you in matters relating to Wi-Fi, please do not hesitate to contact us.













































